On October 11, 2022, Coconut Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences(CRICATAS) published online a paper entitled "UHPLC-MS/MSidentification, quantification of flavonoid compounds from Areca catechu L. extracts and in vitro evaluation of antioxidant and key enzyme inhibition properties involved in hyperglycemia and hypertension" by the journal of Industrial Crops and Products (IF=6.449). This study was the first to systematically identify the flavonoids in the extracts of arecanut flower, husk and seed, and to compare the different pharmacological activities of the three extracts.
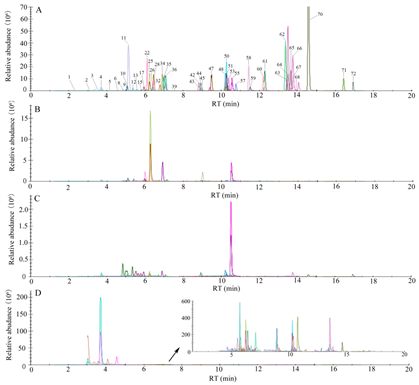
Arecanut (Areca catechu L.) is one of the largest industrial crops in Hainan Province and the top of the "Four Southern Medicines". To help the arecanut industry develop sustainably, it was proposed in Hainan government work report several times that the medical property of arecanut should be explored and industrially applied more. There are varieties of bioactive substances such as alkaloids, polyphenols and polysaccharides. However, the bioactive ingredients and pharmacological activities of arecanut were still need to be systematically explored. In this study, three extracts were prepared from arecanut flowers, husk and seeds, respectively. 72 flavonoids, were detected in arecanut extracts. Orientin, isoorientin, vitexin and schaftoside were found for the first time in arecanut; there were significant differences in the flavonoid compositions of among the three extracts, as arecanut seed extract contained higher contents of catechin, procyanidin B1, procyanidin B2 and L-epicatechin; the flower extract possesses higher contents of luteolin and diosmetin, while the husk extract has higher contents of diosmetin and schaftoside.
Fig. 1. Extracted ion chromatogram (EIC) of 55 flavonoid compounds in sample of standard substance (A), arecanut flower (B), arecanut husk (C) and arecanut seed (D) (positive mode)
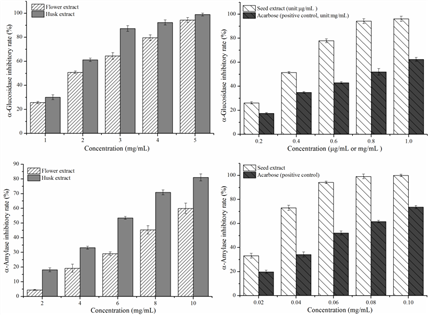
The study explored some biological activities of the three arecanut extracts. The seed extract displayed the strongest inhibitory effect on α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities, which were significantly stronger than those of acarbose, respectively. At the same time, the seed extract also exhibited a strong angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory properties. In conclusion, compared with the extracts from arecanut flower and husk, the arecanut seed extract contained higher contents of total phenols and flavonoids, and has better potential to as an antidiabetic agent and a hypotensor. All the findings above provide relevant data to promote the development of arecanut in medical use .
The associate researcher Song Fei from Coconut Research Institute of CATAS is the first author of the paper, and Associate researcher Tang Minmin is the corresponding author. This research was sponsored by Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences.
Fig. 2. The inhibitory rate of extracts from different parts of arecanut (flower, husk, seed) and (positive control) on α-glucosidase (A, B) and α-amylase (C, D) activity. Different alphabets (a-j) among bars are significantly different at P < 0.05.
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926669022012705?dgcid=author